 |
| Microsoft Excel |
Today, The Grandma is preparing her new course of Microsoft Excel that she is going to start tomorrow. She manages lots of business and she has thought that learning Ms. Excel is a good way to control and manage her own accounting.
The Grandma is able to understand Catalan, Spanish and English and she has decided to use these three languages in her new courses without distinction: tutorials in English and Spanish and exercises in Catalan, English and Spanish (functions). She is going to work with Ms. Excel 2016 although the explanations are available in 2013 and 2010 versions, too.
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet developed by Microsoft for Windows, macOS, Android and iOS. It features calculation, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a macro programming language called Visual Basic for Applications. It has been a very widely applied spreadsheet for these platforms, especially since version 5 in 1993, and it has replaced Lotus 1-2-3 as the industry standard for spreadsheets. Excel forms part of the Microsoft Office suite of software.
Microsoft Excel has the basic features of all spreadsheets, using a grid of cells arranged in numbered rows and letter-named columns to organize data manipulations like arithmetic operations. It has a battery of supplied functions to answer statistical, engineering and financial needs.
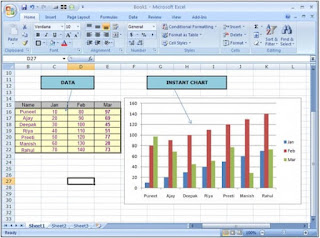
In addition, it can display data as line graphs, histograms and charts, and with a very limited three-dimensional graphical display. It allows sectioning of data to view its dependencies on various factors for different perspectives, using pivot tables and the scenario manager.
It has a programming aspect, Visual Basic for Applications, allowing the user to employ a wide variety of numerical methods, for example, for solving differential equations of mathematical physics, and then reporting the results back to the spreadsheet.
 |
| Microsoft Excel |
It also has a variety of interactive features allowing user interfaces that can completely hide the spreadsheet from the user, so the spreadsheet presents itself as a so-called application, or decision support system (DSS), via a custom-designed user interface, for example, a stock analyzer, or in general, as a design tool that asks the user questions and provides answers and reports.
In a more elaborate realization, an Excel application can automatically poll external databases and measuring instruments using an update schedule, analyze the results, make a Word report or PowerPoint slide show, and e-mail these presentations on a regular basis to a list of participants. Excel was not designed to be used as a database.
Microsoft allows for a number of optional command-line switches to control the manner in which Excel starts.
Excel 2016 has 484 functions. Of these, 360 existed prior to Excel 2010. Microsoft classifies these functions in 14 categories. Of the 484 current functions, 386 may be called from VBA as methods of the object WorksheetFunction and 44 have the same names as VBA functions.
Excel supports charts, graphs, or histograms generated from specified groups of cells. The generated graphic component can either be embedded within the current sheet, or added as a separate object.
These displays are dynamically updated if the content of cells change. For example, suppose that the important design requirements are displayed visually; then, in response to a user's change in trial values for parameters, the curves describing the design change shape, and their points of intersection shift, assisting the selection of the best design.
More information: Aula Clic (Spanish Course)
Excel offers many user interface tweaks over the earliest electronic spreadsheets; however, the essence remains the same as in the original spreadsheet software, VisiCalc: the program displays cells organized in rows and columns, and each cell may contain data or a formula, with relative or absolute references to other cells.
Excel 2.0 for Windows, which was modeled after its Mac GUI-based counterpart, indirectly expanded the installed base of the then-nascent Windows environment. Excel 2.0 was released a month before Windows 2.0, and the installed base of Windows was so low at that point in 1987 that Microsoft had to bundle a runtime version of Windows 1.0 with Excel 2.0. Unlike Microsoft Word, there never was a DOS version of Excel.
Excel became the first spreadsheet to allow the user to define the appearance of spreadsheets -fonts, character attributes and cell appearance. It also introduced intelligent cell recomputation, where only cells dependent on the cell being modified are updated, previous spreadsheet programs recomputed everything all the time or waited for a specific user command.
Excel introduced auto-fill, the ability to drag and expand the selection box to automatically copy cell or row contents to adjacent cells or rows, adjusting the copies intelligently by automatically incrementing cell references or contents. Excel also introduced extensive graphing capabilities.
More information: Excel Exposure (English Course)
The outside perception and inside perception
of Microsoft are so different.
The view of Microsoft inside Microsoft is
always kind of an underdog thing.
Bill Gates
No comments:
Post a Comment